No. 789,255 – Convertible Plane (Sidney C. Carpenter) (1905)
UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE.
_________________
SIDNEY C. CARPENTER, OF WEST HARTFORD, CONNECTICUT.
CONVERTIBLE PLANE.
_________________
SPECIFICATION forming part of Letters Patent No. 789,255, dated May 9, 1905.
Application filed September 1, 1904. Serial No. 223,046.
_________________
To all whom it may concern:
Be it known that I, SIDNEY C. CARPENTER, a citizen of the United States, residing at West Hartford, in the county of Hartford and State of Connecticut, have invented certain new and useful Improvements in Convertible Planes; and I do declare the following to be a full, clear, and exact description of the invention, such as will enable others skilled in the art to which it appertains to make and use the same.
My invention relates to convertible planes of that character designed to be used for planing curved or flat surfaces; and the objects of same are to provide a plane with a spring bearing-surface which may be readily and quickly adjusted to the required degree to bear upon surfaces of more or less curvature and which may be readily converted into a plane of the ordinary or usual construction provided with a flat bearing-surface.
Another object is to provide a plane of this character which may be quickly and accurately adjusted for use under varying conditions and which will be provided with means for adjusting cutting-blades or bits relatively, accurately, and quickly.
These and other objects are attained by means of the construction illustrated in the accompanying drawings, in which —
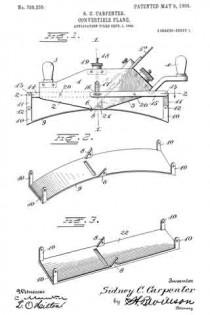
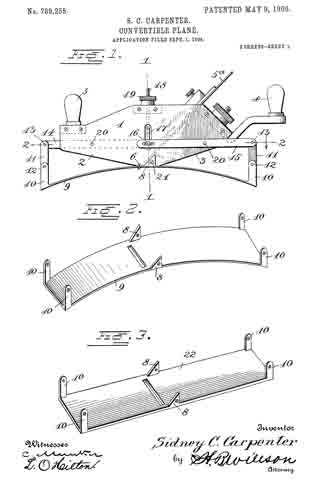
Figure 1 is a side view of a plane constructed in accordance with my present invention and having the curved spring bearing-plate secured thereto. Fig. 2 is a perspective view of the spring bearing-plate detached from the plane. Fig. 3 is a perspective view of the fiat plane-surface which may be substituted for the spring when it is desired to convert the device into an ordinary plane. Fig. 4 is a vertical section on the line 1 1, Fig. 1. Fig. 5 is a longitudinal section on the line 2 2, Fig. 1.
Referring to the drawings for a more particular description of my invention, the numeral 1 designates the body portion of the plane, said body portion being oppositely inclined in front and rear, as shown at 2 3, and provided with suitable handles 4 5 and a cutter or bit 5a. A transverse slightly-curved surface 6 is provided at the central lower portion of the stock or body, and a lug 8, extending upward from the curved steel plate 9, is secured to the stock by a bolt 21, said plate forming the bottom or bearing surface of the plane. Near opposite ends of the plate 9 are lugs 10, projecting upward, said lugs being connected to links 11, pivoted at 12 and connected at their upper ends at 13 to longitudinal levers 14 and 15. Said levers 15 extend toward the middle of the frame upon opposite sides thereof and are connected by a pin 16, extending through the body or stock of the plane and through the front levers 14, a link 17 connecting said levers with a pivoted bolt 18, having fitted thereon a nut 19 for adjusting the levers 14 15 upon their pivots 20 to raise or lower the links 11, and thus adjust the spring-plate 9 to the required curvature for the work to be operated upon.
If it is desired to convert the plane into one of ordinary construction, the bolt 21 may be removed and the plate 22 substituted for the spring-plate in an obvious manner.
From the foregoing it will be obvious that my plane is of comparatively simple construction and may be readily converted from a circular to a flat-bottom plane. The curved steel plate may be readily adjusted to the required degree, depending upon the degree of curvature of the work to be performed.
Having thus described my invention, what I claim as new, and desire to secure by Letters Patent, is —
A plane comprising a stock having oppositely-inclined bottom faces, a spring face-plate secured to said stock between said inclined surfaces, said face-plate having upwardly-extending end lugs, links pivoted to said lugs, levers pivoted to said links and extending longitudinally to the center of the stock, a pin connecting the meeting ends of said levers, a link connected to said pin, a bolt connected to said link, and a nut for adjusting the bolt, the levers and the spring, substantially as described.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand in presence of two subscribing witnesses.
SIDNEY C. CARPENTER.
Witnesses:
JOSEPH P. KENNEDY,
JOHN D. WOOD.