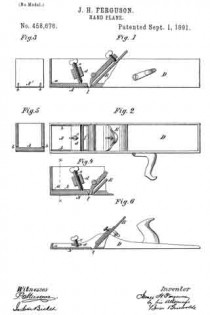
No. 458,676 – Hand-Plane (James H. Ferguson) (1891)
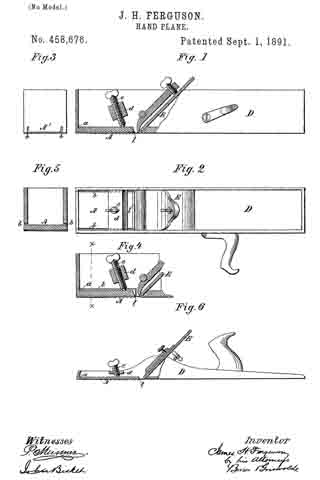
No. 458,676 – Hand-Plane (James H. Ferguson) (1891)
UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE.
_________________
JAMES H. FERGUSON, OF BROOKLYN, NEW YORK.
HAND-PLANE.
_________________
SPECIFICATION forming part of Letters Patent No. 458,676, dated September 1, 1891.
Application filed April 16, 1889. Serial No. 307,485. (No model.)
_________________
To all whom it may concern:
Be it known that I, JAMES H. FERGUSON, of Brooklyn, in the county of Kings and State of New York, have invented a certain new and useful Improvement in Hand-Planes, of which the following is a specification.
My improvement is designed more particularly for planing the sides of electrotype or stereotype plates, but it may be employed for other purposes.
In the accompanying drawings, Figure 1 is a side elevation, partly in section, showing a plane embodying my improvement. Fig. 2 is a plan or top view of the same. Fig. 3 is an end view of the same. Fig. 4 is a sectional elevation illustrating a modification, certain of the parts being broken away to save space. Fig. 5 is a vertical section of the same, taken on the line x x, Fig. 4, certain of the parts shown in Fig. 4 being removed. Fig. 6 is a view in elevation, partly in section, illustrating how my improvement may be employed with another kind of plane.
Similar letters of reference designate corresponding parts in all the figures.
In the example of my improvement illustrated in Figs. 1, 2, and 3 the body of the plane is made in the form of a box and is formed of a single piece of metal — as, for instance, by casting. Near its forward end the face of the plane is provided with an elastic portion A, which normally occupies an elevated position, but which may be pressed downwardly at its inner end portion l, so as to regulate the depth of cut which will be made by the plane-iron E. In order to cause the requisite degree of elasticity, the portion A is separated throughout its length and upon its sides from the sides of the plane-body D by slits or slots b, which extend through the metal of the portion A and upwardly through the end A’ of the plane-body D. It will be seen that by pressing downwardly the inner end portion of the portion A its position may be deflected to any desired extent in order to increase the depth of cut which will be made by the plane-iron. In order to accomplish this deflecting of the portion A, I have shown a screw e, having bearings in a cross-piece d, secured in the sides of the plane-body. By manipulating this screw the deflecting or bending of the portion A may be regulated to any desired extent.
In the example of my improvement shown in Figs. 4 and 5 the operation is precisely like that just described; but there is some slight difference in the mode of constructing the slit or slot b. In this example the slot extends along the sides of the plane-body and downwardly at the inner end of the portion A. Of course the outer end of the portion A is not separate from the sides of the plane-body, except to the thickness of the sides of the body.
In Fig. 6 I have shown the application of the improvement to a so-called “jack-plane” having a body of cast metal. When used with the jack-plane, either one of the means for separating the portion A, so that it will be elastic, may be employed which I have described in the other examples of my improvement shown. I have, however, illustrated that as shown in Figs. 1, 2, and 3.
In all the examples of my improvement shown the portion A when occupying a normal position stands back slightly from the other part of the face of the plane, so that when in such a position the plane-iron will be capable of making its maximum cut.
It will be seen that by my improvement I provide a very inexpensive and ready means for varying the depth of cut which may be made by the plane-iron without going to the necessity of adjusting the plane-iron separately; or, in other words, the plane-iron once having been set it will not be necessary to alter it in order to obtain any desired adjustment for depth of cut.
What I claim as my invention, and desire to secure by Letters Patent, is —
The combination, with a plane-body made in one integral piece and having a portion of its face near one end elastic, but formed integral therewith, of an adjusting device operating upon said elastic portion to cause a deflection thereof, said elastic portion normally occupying a position whereby it is set in beyond the face, substantially as and for the purpose specified.
JAMES H. FERGUSON.
Witnesses:
FREDK. HAYNES,
JOHN BICKEL.