No. 88,109 – Improvement In Plane-Guide (John Woodville) (1869)
United States Patent Office.
JOHN WOODVILLE, OF CINCINNATI, OHIO.
Letters Patent No. 88,109, dated March 23, 1869.
_________________
IMPROVEMENT IN PLANE-GUIDE.
_________________
The Schedule referred to in these Letters Patent and making part of the same.
_________________
To all whom it may concern:
Be it known that I, JOHN WOODVILLE, of Cincinnati, in the county of Hamilton, and State of Ohio, have invented a new and useful Improvement in Plane-Guide and Holder; and I do hereby declare that the following is a full, clear, and exact description thereof, which will enable others skilled in the art to make and use the same, reference being had to the accompanying drawings, forming part of this specification, in which —
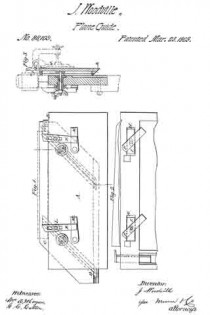
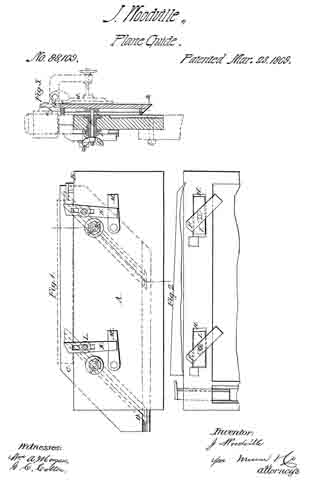
Figure 1 represents a back-side elevation of my improved apparatus;
Figure 2 represents afront-side elevation, with a part broken away; and
Figure 3 represents a transverse section taken on the line x x of fig. 1.
Similar letters of reference indicate like parts.
The object of this invention is to provide an adjustable holder, or clamp, for holding strips, for dressing them, and which will also serve as a guide for straightening or tapering them. It is designed more particularly to be used with the improved joiners’ plane, patented to me, November 6, 1866.
It consists of a holding-strip, or board, which is designed to be secured to a bench, with one edge upward, and which is provided with an adjustable gauge upon one side, against which the strips to be planed are clamped, by buttons and wedges on the other side of the first-mentioned holding-strip.
A represents the holding-strip, which may be secured to a bench, or in a vise, in any suitable manner, with the edge B upward.
C represents a guide and clamping-strip, which is provided with the T-headed inclined grooves D, whereby it is clamped to the strip A, by the bolts E and thumb-nuts E’; the heads F of the said bolts being arranged loosely thereon, and sliding in the wide part of the grooves D.
The holes through the strips A are elongated, and provided with the hollow bolts I, having enlarged heads arranged in the recesses H. The bolts E pass through these hollow bolts, and the office of the latter is to serve as rigid supports for the former when adjusted to the light position, and screwed up tightly by the nuts I’.
K represents clamping-buttons adjustably connected to the front face of the strip A, by the long bolts L; and
M represents wedges pivoted to the face of the strip A, in a position to be conveniently adjusted under the inclined ends of the buttons, for clamping them against the stuff to be operated upon.
The operation is as follows:
When it is designed to dress a strip with parallel and square edges, the guiding-strip C, which is provided with one edge a, and one bevelled edge b, is adjusted to the strip A, with the square edge a as high above the strip A as the designed width of the strip to be dressed the edge a being in a horizontal plane parallel with the edge of the strip A when it is clamped tight thereto by the bolts E and thumb-nuts E’.
The strip to be dressed is then placed upon the upper edge of the strip A, and clamped between the guide C and the buttons K.
The plane, which, according to the improvements patented to me as above described, is provided with an adjustable guide, d, is then placed upon the strips to be dressed, and held by the said guide, so that the edge e of the stock will project over the guide C sufficiently to arrest the cutting-action of the plane when the strip has been worked down to the point coincident with the edge of the guide C.
Any number of strips may thus be dressed to the same gauge with great uniformity, while at the same time the edges will be exactly square, if the plane-guide be adjusted to that angle.
If it is desired to dress the strips with bevelled edges, the bevelled edge b, of the guide G, is placed upward, as represented in blue lines, at b’; and if it be desired to produce tapered strips, the guide C may be adjusted to produce any taper, by loosening the bolts E and I, so as to allow the plates I to move in the recesses H, to correspond with the varying distances caused between the points of contact with the grooves D, of the heads of the bolts E, by changing the horizontal plane of the guide C.
In dressing thin strips, two or any other number, not wider in the aggregate than the plane-bit, may be clamped together, and dressed at once.
In dressing strips in this manner, in my improved guide and holder, with my improved planes, I have found it very desirable to provide the jack, or roughing-plane with an adjustable gauging-strip, f, as shown in red in fig. 3, for the purpose of arresting the cutting-action of the plane-bit, the amount of a few shavings, before the strips are brought down to a level with the upper edge of the guide C, so that the roughing-plane may be removed in time to finish the work by the jointer, which I provide with a similar guide, d, but not with the guide f
The latter may be adjustably connected to the stock, so that, as the latter wears away, it may be adjusted thereon.
I am aware that clamps have already been arranged upon carpenters’ benches in such a rnanner as to be adjustable for cutting different widths of boards with square or bevelled edges.
Having thus described my invention, I claim as new, and desire to secure by Letters Patent —
1. The combination of the clamping-bolts E and the sliding bolts I, with the supporting-strip A and grooved strip C, whereby said strips are held together, for dressing a board with either parallel or tapering sides, substantially as herein shown and described.
2. The combination, with the strips A and G, of the adjustable buttons K and pivoted wedges M, substantially as and for the purpose set forth.
JOHN WOODVILLE.
Witnesses:
FRANK BLOCKLEY,
ALEX. F. ROBERTS.