No. 716,386 – Plane (Maschil D. Converse) (1902)
UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE.
_________________
MASCHIL D. CONVERSE, OF NEW YORK, N. Y., ASSIGNOR TO
JOHN J. TOWER, OF MONTCLAIR, NEW JERSEY.
PLANE.
_________________
SPECIFICATION forming part of Letters Patent No. 716,386, dated December 23, 1902.
Application filed October 29, 1901. Serial No. 80,470. (No model.)
_________________
To all whom it may concern:
Be it known that I, MASCHIL D. CONVERSE, a citizen of the United States, residing at New York, borough of Manhattan, in the county and State of New York, have invented new and useful Improvements in Planes, of which the following is a specification.
My invention relates to improvements in planes, and more particularly to means for securing and adjusting the irons thereof; and the objects of my invention are to improve the efficiency of such and to simplify the construction and reduce the cost of manufacture.
My invention is comprised in certain novel mechanisms, construction, arrangement, and combinations of parts hereinafter fully set forth and claimed.
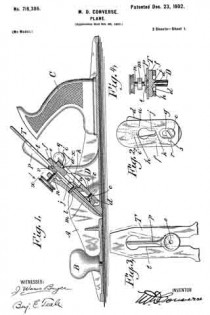
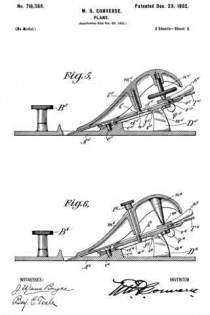
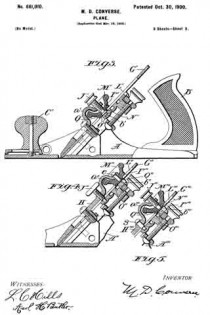
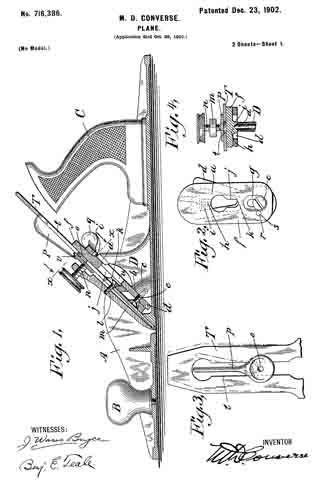
In the drawings, Figure 1 is a longitudinal vertical sectional elevation of a plane, of a type commonly known as “iron corrugated-bottom” planes, showing my invention incor-porated. Fig. 2 is a plan view of important parts of my invention, compassing the principal means for accomplishing vertical adjustment of the plane-iron. Fig. 3 is a plan view of the plane-iron and lateral-adjustment mechanism. Fig. 4 is a cross-section on line x x of Fig. 1; and Figs. 5 and 6 are views, partly sectional, illustratrating modilied constructions of my invention, all showing construction, application, and operation of my invention, as will be hereinafter more fully set forth in detail.
My invention may be applied to all types of planes, although I have shown it as applied to iron planes, as hereinbefore stated.
Planes have been made with mechanisms for vertical adjustment of the irons comprising bell-crank members and transverse grooves in the plane-irons to be engaged thereby pivoted to the body. Others have been made with mechanisms for vertical adjustment of the irons comprising bell-crank members and transverse slots in the plane-irons to be engaged thereby and pivoted to the body above the fulcrum-screw, and still others have been made with mechanisms for vertical adjustment of the irons comprising bell-crank members pivoted through the longitudinal slot of the plane-iron to a bed-piece at points above the fulcrum-screw and in engagement with notches in the cap-plate. Planes of such construction are expensive of manufacture, involving careful and accurate dimensioning of the throat and finishing of the ways and channels by difficult and tedious machining. In my present invention I overcome these disadvantages by novel arrangement and form of parts, dispensing entirely with the notches in the cap-plate and with the transverse grooves or slots in the plane-irons, rendering it wholly unnecessary to perform any expensive machining or fitting to compass a proper and accurate adjustment and holding of the plane-irons, all of which will be clearly seen and understood by those skilled in the art from the descriptions following.
Like letters indicate corresponding parts throughout the several figures.
A is the body of the plane, B a knob attached to the front portion thereof, and C the handle proper attached to the rearward portion.
D is a post and saddle-rest, which in case of iron-body planes is preferably cast integral centrally thereof. The apex of this post l prefer to make A-shaped, (distinctly shown at a, particularly in Fig. 4,) and the face thereof sloped to correspond with the incline b at its forward and broadened base c, the latter forming pivotal points and a rest for the extreme lower end of a vertical-adjustment lever d, which is pivoted thereto by a screw e. Upon the flattened upper surface of the pivoted end of the lever d rests the lower end of a flat saddle-plate f, which lower end is slotted longitudinally and recessed or countersunk on the upper side at g to receive the said pivot-screw e, which also serves to hold it in place, though admitting of a vertical sliding movement. Adjacent to the upper end of this saddle on the nether side a projection i is cast or formed, and a V-shaped groove h is formed therein to rest in slidable engagement with the sloping A-shaped apex a of the post D, which also serves to retain the same against lateral movement, a condition necessary for the carrying out of part of my invention. At a point centrally thereof and between the V-grooved projection i and above the slot g and pivot e is another opening in the saddle at j, the narrower lowermost end of which is recessed or countersunk on the under side at k to receive the head of the fulcrum screw or stud l when the same is slipped under the laterally-overhanging edges thereof. This fulcrum screw or stud l is secured in a clamping-plate m from its under side, (and I prefer to use a screw for convenience of adjustment.) In the upper end of the clamp-plate is a gnarled-head cramp-screw n, the rounded end of which engages a depression o of a lateral-adjustment lever p, serving as a pivot therefor. The vertical-adjustment lever d is provided at its upper end with a button q for operating. Midway of the ends and laterally of the slot g in the saddle f there is a hole r (see Fig. 2) for reception of a stud s, (freely fitting it, see same figure,) which stud is fixed (preferably rigidly) upon or in the vertical-adjustment lever d at a like position laterally relatively the axis thereof and pivot-screw e. This stud s and the hole r are located on a transverse line at right angles to the longitudinal vertical centers of the lever d and sliding saddle f, respectively, directly opposite the center of the pivot-screw e and sufficiently distant therefrom that it may not bind by describing an arc of too small a radius when the lever is operated.
For convenience and so that post D and projection i may not interfere therewith the lever d is open or divided at u and joined again above at the button q.
T is the plane iron or bit, which has a slot t longitudinally its center to admit of passage of the head and shank of the fulcrum-screw l therethrough.
In the modifications shown by Figs. 5 and 6 the principles of my invention hold, these modifications being such as render my invention applicable to what are known as “block-planes.” In the case of Fig. 5 the cramp-screw n5 is inverted and screw~socketed within and on the under side of the shell-like extension of the clamp-plate m5. The gnarled head of the screw being enlarged somewhat is accessible from the lateral sides, while in the case of Fig. 6 instead of a cramp-screw a projecting point n6 serves to engage the lateral-adjustment lever p6 as its pivot, and a gnarled head cramp-screw l6 is entered from the forward upper side through the clamp-plate m6 and engages a threaded hole k6 in the saddle f6.
The operation of my invention is as follows: To raise or lower the plane-iron T, push the button q to the left or right hand, which will cause the stud s to carry the saddle f up or down as the lever is rocked on its axis at e. To square the cutting end of the plane iron or bit with the throat of the plane, push the lever p to the right or left, as may be required, which causes the eccentric v to move the bit till the desired lateral adjustment is had. All these movements may be made without loosening the cramp-screw.
I do not limit myself to the specific form of the vertical-adjustment lever described herein, except that it should be located beneath the saddle f, which rests upon its lower end, and have its pivotal axis e and saddle-engaging stud s at its lowermost end or below the transverse plane of the fulcrum-screw and the apex of the post D, nor do I limit myself to the particular form of the post or of the saddle herein described, as manifestly they may be modified without departing from the spirit of my invention.
It will be readily understood by those skilled in the art that the novel construction and arrangement of the parts in my present invention, as well as their simplicity, make it possible to cast the same in metal to substantially finished form and dimensions, excepting the screws, thus saving the laborand cost of fitting.
I do not herein claim the lateral-adjustment mechanism shown, except in combination with the leading features of my present invention, for the reason that the same was allowed to me broadly by Letters Patent of the United States No. 619,394, dated February 14, 1899; but,
Having described my invention, what I do claim as new, and desire to secure by Letters Patent, is —
1. In a plane a vertical-adjustment mechanism comprising a laterally-movable lever pivoted centrally to the plane-body at a point below the transverse plane of the fulcrum-screw and of the apex of the post; a stud located thereon on the top side and laterally opposite its axis, a saddle engaged by said stud held in place by the pivot-screw of said lever, and slidably resting upon the pivoted end of the same and upon the apex of a post above said fulcrum-screw, in combination with a plane-iron and means for clamping the latter upon said saddle.
2. In a plane a laterally-movable lever pivoted centrally to the plane-body at a point below the transverse plane of the fulcrum-screw and of the apex of the post; a stud located thereon on the outer side and laterally opposite its axis; a saddle engaged by said stud held in place by the pivot-screw of said lever and slidably resting upon the pivoted end of the same and upon the apex of a post, above said fulcrum-screw; a plane-iron and means for clamping the same upon said saddle, in combination with mechanism for lateral adjustment of the plane-irons.
3. In a plane a vertical-adjustment mechanism comprising a laterally-movable lever pivoted centrally to the plane-body at a point below the transverse plane of the fulcrum-screw and of the apex of the post; a saddle slidably resting upon the pivoted end of said lever and upon the apex of a post; a laterally-located stud operatively connecting said saddle and said lever below the transverse plane of the fulcrum-screw, and a plane-iron, in combination with a lateral-adjustment lever eccentrically pivoted at the upper end of a clamp-plate.
4. In a plane a vertical-adjustment mechanism comprising a laterally-movable lever pivoted at its lower end; a saddle slidably resting upon the pivoted end of said lever and upon the apex of a post removed from the pivoted end of said lever, in combination with means for operatively connecting said lever and said saddle at their respective lower ends to accomplish vertical movement of the latter.
5. In a plane a laterally-movable pivoted vertical-adjustment lever, having an opening u centrally thereof, in combination with a saddle operatively engaged by said lever and having a groove h longitudinally central thereof on its under side contacting with the apex of a central post D within the plane-body and held in place by the pivotal screw of the lever.
6. In a plane a laterally-movable pivoted vertical-adjustment lever, having an opening fa centrally thereof, in combination with a post D projecting within said opening.
MASCHIL D. CONVERSE.
Witnesses:
WARREN W. WHITNEY,
J. MEACH.