No. 1,032,346 – Plane (Edmund A. Schade) (1912)
UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE.
_________________
EDMUND A. SCHADE, OF NEW BRITAIN, CONNECTICUT, ASSIGNOR TO THE STANLEY RULE &
LEVEL COMPANY, OF NEW BRITAIN, CONNECTICUT, A CORPORATION OF CONNECTICUT.
PLANE.
_________________
1,032,346. Specification of Letters Patent. Patented July 9, 1912.
Application filed November 1, 1911. Serial No. 657,934.
_________________
To all whom it may concern:
Be it known that I, EDMUND A. SCHADE, a citizen of the United States, residing at New Britain, county of Hartford, State of Connecticut, have invented certain new and useful lmprovements in Planes, of which the following is a full, clear, and exact description.
My invention relates to improvements in planes, and particularly to that type of plane in which the main body or stock is formed of wood.
My improvement aims at providing an improved construction for reinforcing the wood stock at the weakest point, namely, at the throat opening, where much of the wood is out away. Incidentally, but none the less important, the means for reinforcing the wood body cooperates in an improved manner with other new features of construction to hold the frog or cutter carrier seat securely in position.
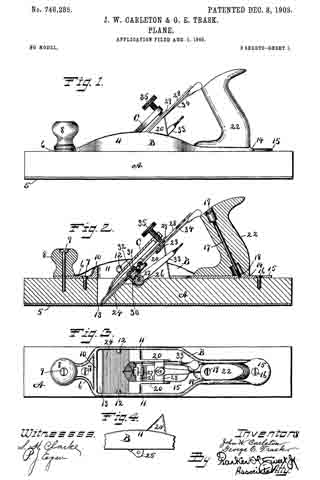
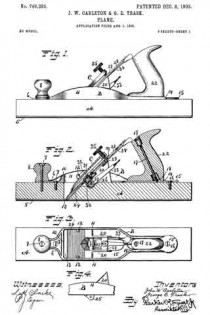
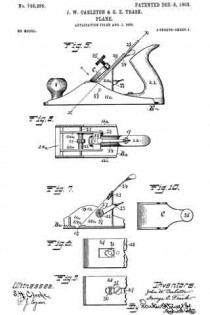
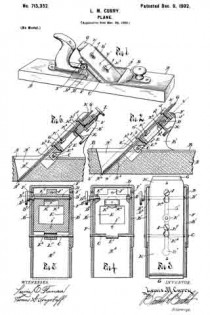
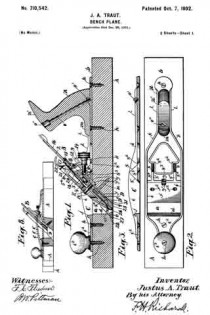
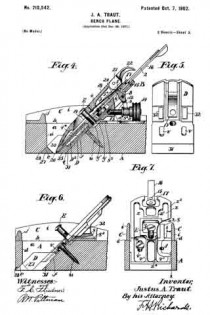
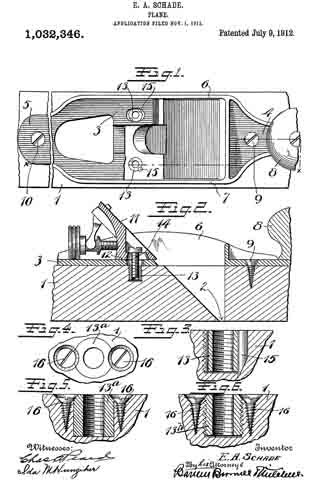
ln the drawings Figure 1 is a plan view of a part of a plane, constructed to embody my invention, the frog and plane iron being removed, the ends of the main reinforcement being broken away. Fig. 2 is a section on the line x–x Fig. 1, showing the cutter carrier, or frog, in place. Fig. 3 is a relatively enlarged sectional view of a detail of construction, on the section y–y Fig. 1. Fig. 4 is a plan view of a modification of the same detail. Fig. 5 is a sectional view of the modified detail shown in Fig. 4. Fig. 6 is a sectional view of still another modification of the same detail.
1 represents the main body or stock of a plane, the same being of substantial length, breadth and thickness, and being formed of wood. At an intermediate point in the length of the main body the stock is cut away down to the throat passage 2 to form a space for the plane iron and for the clearance of shavings. This cut-away portion always tends, in planes of this character, to substantially weaken the stock 1. To reinforce and strengthen said stock 1, I apply to the top side thereof a metal bracing or reinforcing piece of peculiar design, including a relatively wide plate 3 terminating in relatively narrowed-in extensions 4–5.
6–7 are integral upright reinforcing ribs bordering the sides of the reinforcing plate and bridging the plane iron passage in said plate and also in said stock. These ribs 6–7 give great rigidity to the reinforcing plate, so that when the same is properly secured to the stock 1, the weakened part thereof, as before pointed out, will be adequately strengthened so as to prevent all danger of breakage.
The usual hand grips may be provided at each end of the plane, the forward grip being shown at 8, the rear grip being omitted for want of room on the drawings.
Both ends of the reinforcing plate are secured to the wood stock 1 by means of screws 9–10. It is obvious that unless the middle portion of the reinforcing plate 3 is adequately secured to the stock, that the latter will not be properly braced. Hence I have provided means which not only serve to secure the plate at a middle point, between the screw fastenings 9–10, to the wood stock, but also serve to effectively hold the frog in any of the adjusted positions without strain upon the reinforcing plate.
11 represents the cutter support or frog, which in general is of well known design, and hence needs no detailed description. 12 represents the base of said frog. In this base, at each side, are provided screw-slots or passages, one of which appears in the upper portion of Fig. 1. Directly under these passages, and securely anchored in the wood stock 1, are cylindrical anchor blocks 13–13 drilled and tapped to receive the clamping screws 14, one of which appears in Fig. 2. The screws 14 pass through longitudinal slots in the frog, and enter the anchor blocks 13. These anchor blocks 13–13 may be shaped on the outside in any desired way, so long as they may be securely embedded and retained in the wood stock 1 in a rigid manner. For example, in the drawings, Figs. 1 to 3, each block 13 is shown as having an external coarse thread, which permits said block to be screwed into the wood stock 1. When said block is screwed down firmly in place, it is held against turning preferably by a pin 15, which acts as a key. The outer side of each block may have one or more vertical grooves or key-ways to permit one side of said key pin 15 to project partly into said anchor block when the latter has been screwed home.
ln Figs. 4 and 5, I have shown a slight modification of the anchor block, in which the outer wall thereof is unthreaded and arranged to be forced directly into a bore in the stock 1. In this modiiication the block is indicated at 13a and is held in place by means of wood screws 16, the upper end of the block being cut away or notched to permit part of the screw-head of each screw 16 to enter the notch and hold the block down in place and at the same time prevent it from turning with the clamping screw 14.
In Fig. 6, I have shown another modification of the block, said block being indicated at 13b, the same being similar to the block 13a with the exception that the outer side is provided with a coarse thread. In this instance the block is held in place against vertical displacement by the screw-threads and against turning by screws 16–16, as in Fig. 5.
The effect of this combination of parts is as follows: When the reinforcing plate is applied to the base 1, it is held at its ends by the screws 9–10, and, while an additional screw or screws may be provided whenever desired, the same are unnecessary, in view of the fact that when the frog 11 is in place and is clamped down by the screws 14, the drag of said screws tends to hold not only the frog 11 tightly on the reinforcing plate 3, but also holds the reinforcing plate 3 rigidly down upon the stock 1. By this arrangement, a long screw-bearing is provided for the clamping screws 14, as would not be the case if the screws 14; relied alone upon threads cut in screw passages on the comparatively thin reinforcing plate 3, for in such a case there would be danger of stripping the threads. Not only is it important to secure a firm and effective anchorage for the clamping screws 14 for the purpose of holding the clamping plate 3 tightly to the stock 1, but it is also important for the purpose of holding the frog 11 tightly upon its seat so as to prevent all danger of chattering of the plane iron. It is clear that it is of the greatest advantage to secure the plate 3 to the wood stock 1 directly at, or as near as possible to, the point where the strain occurs. Since the anchor blocks 13–13 are arranged closely adjacent to the rear of the plane iron passage in the reinforcing plate, it is obvious that a maximum of resistance to strains is adorded at this point, whereby the frog, top iron and stock 1 are securely braced at a point close to the mouth or cutter passage.
From the foregoing it will be observed that the plane of stress of the clamping screw or screws is always within the zone of resistance against upward movement of the means for holding the anchoring device, and it is also apparent that the plane of stress of said clamping screws is in advance of the rear fulcrum of the frog, hence the frog cannot by any possibility yield and chatter by any upward pressure applied to the front portion of the frog, as when the plane is in use.
What I claim is:
In a plane of the character described, a wood stock having a cutter passage extending through the same from the top to the bottom at a point intermediate its ends, an anchoring means rigidly embedded in said stock close to the rear of said cutter passage, means for holding said anchoring means from movement in any direction in said stock, a frog mounted on said stock at the rear of said cutter passage, and a clamping screw passing through said frog and arranged to screw into said anchoring means, said frog having a longitudinally slotted passage for said clamping screw to permit adjustment fore and aft, the plane of stress of said clamping screw being with-
in the zone of resistance to upward movement of the anchor holding means and forward of the rear fulcrum of said frog.
EDMUND A. SCHADE.
Witnesses:
I. W. CHAPMAN,
W. J. WORAM.
Copies of this patent may be obtained for five cents each, by addressing the “Commissioner of Patents, Washington, D. C.”
_________________