No. 799,234 – Carpenter’s Plane (John Jett) (1905)
UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE.
_________________
JOHN JETT, OF SAN FRANCISCO, CALIFORNIA.
CARPENTER’S PLANE
_________________
799,234. Specification of Letters Patent. Patented Sept. 12, 1905.
Application filed August 18, 1904. Serial No. 221,296.
_________________
To all whom it may concern:
Be it known that I, JOHN JETT, a citizen of the United States, and a resident of San Francisco, in the county of San Francisco and State of California, have invented certain new and useful Improvements in Carpenters’ Planes, of which the following is a specification.
The objects I have in view are, first, to produce an adjustable plane in which the bit or plane-iron is held more firmly and is more easy to adjust than heretofore; second, to produce an adjustable plane in which the different parts are less liable to become disarranged than heretofore; and to this end the main feature of my invention consists in providing a roller which extends across the plane in front of the bit and about midway between the top and bottom of the plane-stock and having an improved gearing between the roller and bit by which the bit is given a slow and positive movement and by which the bit is held in any position without the use of any locking device.
Another feature is to have the roller connected to a lever on the outside of the stock and have a lug to hold the lever in place and prevent end movement of the roller.
Another feature is to provide a hood above the roller to protect, strengthen, and afford a continuous bearing for the same.
Another feature is to hold the bit and cap-plate more firmly together so they will not become disarranged when the bit is carried under the roller.
Another feature is to have the gearing adjustably attached to the cap-plate, so that the lever will occupy a convenient position when the bit is clamped to the stock.
These features are more fully described in the following specification, reference being had to the accompanying drawings, which form a part thereof.
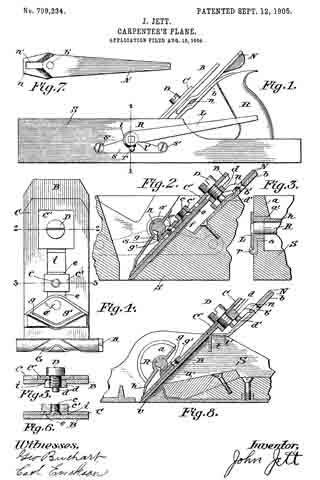
Figure 1 is a side view of my improved plane ready for use. Fig. 9. is a longitudinal sectional view of the central part of the plane, showing the mechanism by which the bit is adjusted. Fig. 3 is an enlarged cross-section of the plane on the line 1 1 of Fig. 1, showing a sectional view near the left-hand side of the plane looking forward, the bit cap-plate and gear-plate not being shown. Fig. A is a top view of the gear-plate, cap-plate, and bit in their proper position, the roller being shown crosswise at the bottom. Fig. 5 is a cross-section on the line 2 2. of Fig. 4. Fig. 6 is a cross-section on the line 3 3 of Fig. 4. Fig. 7 is a top view of the lever for adjusting the bit sidewise. Fig. 8 is a longitudinal sectional view of the adjusting mechanism as applied to metal plane-stocks.
Similar letters refer to similar parts throughout the several views.
In the drawings, the letter S represents the plane-stock, which is cutout at the middle to receive the bit, the same as in the old-style wooden-wedge plane-stock. The stock is then cut to receive the bushing x, of which there is one on each side of the stock, and is held thereto by the screws x’, which enter the solid part of the stock, as shown in Fig. 2. The bushing serves as a bearing to receive the roller R, which extends through the stock about midway between the top and bottom in front of the bit. The roller is actuated by the lever L, which is rigidly attached thereto and is usually placed on the left-hand side of the plane, as shown in Fig. 1. These parts are held in place by the lug r on the bushing, a part of this lug being cut away to receive the beveled part l on the lever, and this beveled part is cutaway, as at l’, so as to pass the lug, and thus allow the roller to be removed and replaced at will.
The roller is provided with a double spiral groove G, Fig. 4, adapted to receive the V-shaped rib g on the gear»plate g’ I prefer to have this rib with a wider angle than the groove in the roller. Then the rib and groove will not be in exact alinement, and the groove itself is cut wider to receive the rib. This will cause the gear-plate to have a slower movement when compared with the roller and will give a finer adjustment of the bit.
The gear-plate is pivoted to the dovetail sliding member e bythe rivet e’. This member slides in the dovetail slot i, Fig. 6, in the cap-plate C and is made adjustable thereto by the bolt c and the nut c’. The cap-plate has a small section C’ cut out near its upper end, and this section is made adjustable to the bit B by the cap-bolt D and the nut d, which moves up and down in the dovetail slot i’ in the bit, and when the bolt is tightened the nut will be wedged into the slot, and thus held more firmly than where it is seated on a flat surface, and when it is desired to sharpen the bit the cap-plate is lifted off the adjustable section without loosening the screw. By this arrangement I dispense with the large hole which is usually placed at one end of the slot in the bit. I therefore make the slot of uniform width, which requires less work and less material.
Above the roller is the hood lt, which serves to protect the gearing and strengthen the roller and gives it a bearing the entire distance between the bushings. It extends from side to side on the inside of the plane, and its cross-section, as shown in Fig. 2, is uniform from side to side. It extends under the abutment a at each side of the plane, as shown in Fig. 3, and I prefer to have the semisleeve a’ on the bushing extend out flush with the abutment, as shown in Figs. 2 and 3, as this connects the hood firmly to the bushings; but this can be dispensed with, if desired. The abutment serves to hold the upper part of the hood firmly down on the roller and the lower part firmly down on the cap-plate, and when the roller is removed the hood is easily taken out.
I prefer to have the bed, or “that part just behind the bit,” cut away, as at f, Fig. 2, so as to allow the bit to spring when it is carried under the roller; but this can be avoided by having the bit curved upward in the middle when out of the plane. Then when it is carried under the roller it will spring almost straight.
The bit can be adjusted sidewise by a pivoted lever, the lower end of which enters the slot in the bit near the cap-screw similar to the ones now in general use; but this requires a long slot, and consequently a long bit, which is undesirable, and to avoid this I provide a lever N, which is pivoted to the brace b by the rivet b’. The lower end of this brace is attached to the stock and the upper end is attached to the handle H. It serves as a brace for the handle and also a support for the lever. The lower end of this lever is pressed or bent upward, as at n, and this part is provided with a slot n’, adapted to receive the lug d’ at the lower end of the cap-bolt. This lug can be attached to the nut d, as shown in Fig. 8, if desired. In either case it is attached firmly to the bit. It will be seen that the raised part n, extends up on each side of the rivet and serves to guide the lug into the slot when the bit is being placed in the stock.
It will also be seen that the old style wooden-wedge plane can be converted to use the mechanism here described and can then be used with the new or the old system, as desired. My improvement is also well adapted for metal plane-stocks, in which no bushing is required. The abutment a, Fig. 8, is cast or riveted on each side above the hood and serves the same purpose as described in the wooden stock. The brace b, instead of being a narrow strip as in the wooden plane, has its lower end widened, so as to extend the entire width of the stock, and is bent into the form of an angle. The vertical part t passes through a slot in the upper edge of the stock and is riveted on the outside. The horizontal part t’ rests on the upper edge of the stock. These two parts serve to hold the brace firmly to the stock and also serve to support the bit, which presses strongly thereon; otherwise the brace serves the same purpose as in the wooden stock. Another feature in this plane is the wooden fender w, attached to the bottom on the inside behind the bit. It may be an extension of the handle or may be a separate piece. It serves to prevent the edge of the bit from being dulled when it is being placed in the stock. Another feature is to pivot the gear-plate direct to the cap-plate and dispense with the dovetail sliding member previously described. This works well where the bottom of the plane is not subject to much wear and where the cap-plate is not shifted through a wide range.
When it is desired to remove the bit, the lever L is moved over to the front end of the stock, causing the gear to release the bit, which can then be taken out and replaced at will.
Having thus fully described my invention, what I claim, and desire to secure by Letters Patent, is —
1. A plane having a plane-iron and a gearing adjustably attached thereto, the gearing consisting of a gear-plate with a V-shaped rib thereon, and having a roller passing through the stock in front of the plane-iron and having a lever attached to the roller on the outside of the stock, and having the roller provided with a double spiral groove adapted to engage the rib on the gear-plate and carry it forward under the roller and thus bind it firmly to the stock.
2. A plane having a plane-iron and a gearing adjustably attached thereto the gearing consisting of a gear-plate with a V-shaped rib thereon and having a roller passing through the stock in front of the plane-iron the roller provided with a double spiral groove with a less angle than the rib on the gear-plate and adapted to engage the rib and carry it forward under the roller and thus bind it firmly to the stock.
3. A plane having a plane-iron and a gearing adjustably attached thereto and having a roller passing through the stock in front of the plane-iron, and having a lever attached to the roller on the outside of the stock and having a lug adapted to hold the lever in place and prevent end movement of the roller and having the roller provided with gearing adapted to engage the gearing on the plane-iron and carry it forward under the roller and thus bind it firmly to the stock.
4. A plane having a plane-iron and a cap-plate and a gearing adjustably attached thereto and having a roller passing through the stock in front of the cap-plate the roller provided with gearing adapted to engage the gearing on the cap-plate and carry it forward under the roller and thus bind it firmly to the stock.
5. A plane having a plane-iron and a cap-plate with a small section cut out near its upper end and having the section adjustably attached to the plane-iron by a bolt and nut the nut being adapted to wedge into the slot of the plane-iron and having a gearing adjustably attached to the cap-plate and having a roller passing through the stock in front of the cap-plate the roller provided with gearing adapted to engage the gearing on the cap-plate and carry it forward under the roller and thus bind it firmly to the stock.
6. A plane having a plane-iron and a gearing adjustably attached thereto and having a roller passing through the stock in front of the plane-iron and having a hood above the roller on the inside of the stock adapted to strengthen the roller and afford a good bearing for the same, the roller provided with a gearing adapted to engage the gearing on the plane-iron and carry it forward under the roller and thus bind it firmly to the stock.
JOHN JETT.
Witnesses:
J. M. EVERS,
S. THORN.