No. 955,556 – Plane (Edmund A. Schade) (1910)
UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE.
_________________
EDMUND A. SCHADE, OF NEW BRITAIN, CONNECTICUT, ASSIGNOR TO THE STANLEY RULE
& LEVEL COMPANY, OF NEW BRITAIN, CONNECTICUT, A CORPORATION OF CONNECTICUT.
PLANE.
_________________
955,556. Specification of Letters Patent. Patented Apr. 19, 1910.
Application filed March 18, 1909. Serial No. 484,099.
_________________
To all whom it may concern:
Be it known that I, EDMUND A. SCHADE, a citizen of the United States, residing at New Britain, county of Hartford, State of Connecticut, have invented certain new and useful Improvements in Planes, of which the following is a full, clear, and exact description.
My invention relates to improvements in planes, the main object being to provide superior adjusting means.
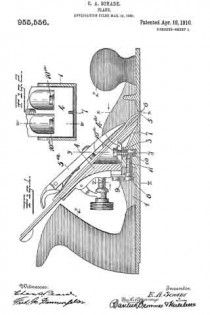
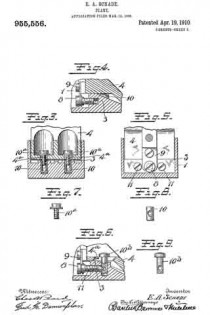
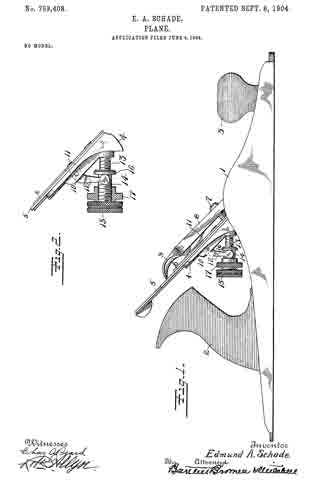
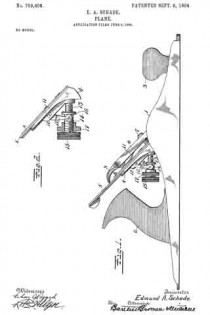
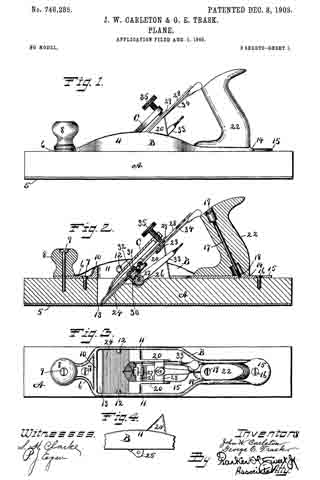
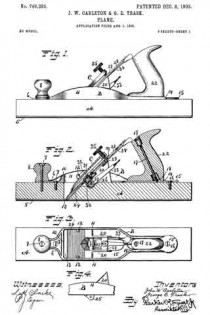
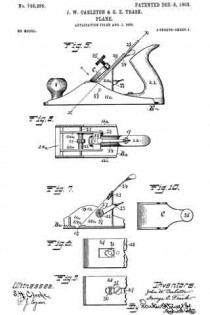
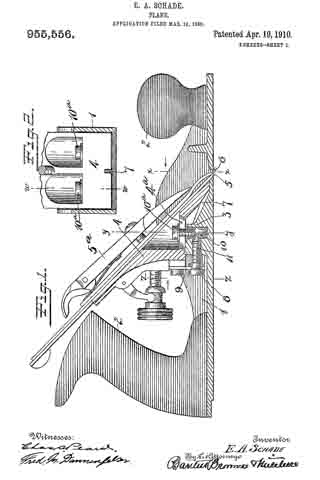
In the accompanying drawings, Figure 1 is a longitudinal section of the body of a plane and certain parts, showing also certain other parts in side elevation, this section being taken on approximately the line W–W Fig. 2. Fig. 2 is a cross-section on the line X–X Fig. 1, looking in the direction of the arrow. Fig. 3 is a cross-section on the line Y–Y Fig. 1, looking in the direction of the arrow. Fig. 11 is a cross-section on the line Z–Z Fig. 1, looking in the direction of the arrow. Fig. 5 is a central longitudinal section of certain parts of the plane. Fig. 6 is a longitudinal section taken on the same plane as the section of Fig. 1 and showing a modiication. Figs. 7 and 8 are side elevations of companion parts. Fig. 9 is a side elevation of a modified part.
1 represents the frame of a plane provided with the usual sole and cheek pieces, and having the usual handles 2–2.
3 is a saddle mounted on the sele of the plane and preferably integral therewith. This saddle 3 furnishes a support for the frog 4, upon which is mounted the plane-iron 5, the same being secured thereto by the well known clamp 5a not necessary to describe in detail herein. The forward or cutting edge of the plane-iron 5 projects through a throat 6 in the sole of the plane. In the particular form shown, the saddle 3 is provided with a rib 7, which enters a groove in the lower end of the frog 4 and so fits the same that it operates as a guide to guarantee an accurate fore and aft movement of the frog relatively to the longitudinal axis of the plane while adjustment is being effected. The frog is suitably shaped to rest upon the saddle 3 so that it may be adjusted back and forth, thereby shifting as desired the cutting edge of the plane-iron 5 forward and back in the throat 6. The usual adjusting mechanism to vary the projection of the plane-iron may be provided, but, since the same constitutes no part of this invention, it need not be described herein.
The particular feature of invention herein disclosed relates to the adjustment of the frog, whereby the throat clearance may be varied. To accomplish the adjustment of the frog, I provide an adjusting screw 8 mounted at the rear of the saddle 3 and operating to and fro. A forked plate 9 carried by and at the rear of the frog 4 stands in an annular groove in the head of the screw 8 so that as the screw 8 is operated to and fro, it imparts a corresponding movement to the frog, provided the latter is not locked in place. To lock the latter in place, I provide a simple and effective clamping mechanism comprising (in the form shown in Figs. 1 to 4 and 6 and 7) the tubular shank 10 arranged vertically in a suitable bore in the saddle 3. As shown, two of these tubular shanks 10 are provided and each of these shanks is preferably threaded to receive a screw 10a, the shank of each screw standing in a longitudinal slot 4a in the frog 4.
11–11 are set-screws which pass into the rear of the saddle 3 so as to be easily accessible from the rear. These screws preferably have conical noses at the forward end, which pass into recesses in the side of each sleeve 10 so that when said screws 11 are advanced they will operate to force the sleeves 10 down so as to clamp the heads of the screws 10a tightly against the frog, in turn drawing the frog hard down against the saddle 3. Ordinarily, in planes of this character, it has been necessary, in order to adjust the frog, to remove the plane-iron 5. Inasmuch as the degree of throat clearance cannot be accurately and quickly determined when the plane-iron is removed, it follows that an adjusting device which is accessible and operable when the plane-iron is in place, furnishes an exceedingly valuable improvement.
By my invention all that is required is to simply loosen the screws 11–11, after which the adjusting screw 8 may be turned in a direction to advance or retract the frog to the desired extent. When the proper adjustment has been attained, the set-screws 11–11 are advanced by a screw-driver entered from the rear, until the heads of the screws 10a draw down on the frog and clamp it firmly to the saddle.
During the period of adjustment, the rib serves to guide the forward edge of the frog to and fro in exactly the proper line, thus relieving all the other parts of this burden. While of course an approximate alinement might be given by the cheek-pieces, it would require an expensive machining operation to so finish the cheek pieces and frog sides that accurate alinement, from this source, could be relied upon. By my invention the rib 7 may be cast integrally with the saddle and the groove in the lower side of the frog which rides on the rib may be quickly and easily formed so as to guarantee the maximum of perfection in adjustment at a minimum of expense and labor.
In the modification shown in Figs. 6 and 9, I provide the solid clamping stud 10b in place of the companion parts 10–10a, and in this case, instead of providing a tubular sleeve similar to 10, I provide a solid shank for the stud 10b.
I am aware that various modifications may be made, and, so long as the construction selected provides for adjustment of the frog without removing the plane-iron therefrom, I deem such modification as within the scope of the broadest of the claims herein.
What I claim is:
1. In a plane, a body portion having a sole and a throat therein, a frog support arranged at the rear of said throat and extending transversely across the sole, a frog mounted on said support, and adjustable to and fro, means for adjusting said frog comprising a screw accessible at the rear of said frog, means to secure said frog on said support comprising a clamping device projecting downwardly through the frog and into said support, a locking device comprising a screw entering said support from the rear, the forward end of said screw having a cone head, a recess in said clamping device into which said cone head may be projected, the inclined wall of said cone head engaging and forcing said clamping device in a direction to rigidly secure said frog in place.
2. In a plane, a body portion having a sole and a throat therein, a frog support arranged at the rear of said throat and extending transversely across the sole, a frog mounted on said support and adjustable to and fro, means for adjusting said frog comprising a screw accessible at the rear of said frog, means to secure said frog on said support comprising a two part clamping device projecting downwardly through the frog and into said support, a locking device comprising a screw entering said support from the rear, the forward end of said screw having a cone head, a recess in said clamping device into which said cone head may be projected, the inclined wall of said cone head engaging and forcing said clamping device in a direction to rigidly secure said frog in place, said clamping device being adjustable as to length.
EDMUND A. SCHADE.
Witnesses:
W. J. WORAM,
I. W. CHAPMAN.