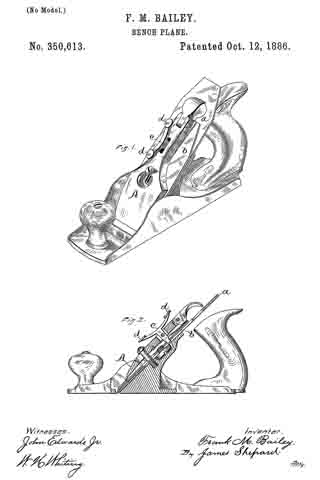
No. 719,051 – Plane (Walter L. Scott) (1903)
UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE.
_________________
WALTER L. SCOTT, OF SAN FRANCISCO, CALIFORNIA, ASSIGNOR TO
THE STANLEY RULE & LEVEL COMPANY, OF NEW BRITAIN, CONNECTICUT,
A CORPORATION OF CONNECTICUT.
PLANE.
_________________
SPECIFICATION forming part of Letters Patent No. 719,051, dated January 27, 1903.
Application filed October 21, 1902. Serial No. 128,125. (No model.)
_________________
To all whom it may concern:
Be it known that I, WALTER L. SCOTT, a citizen of the United States, residing at San Francisco, in the county of San Francisco, State of California, have invented certain new and useful Improvements in Planes, of which the following is a full, clear, and exact description.
This invention relates to improvements in planes, and particularly to plane-handles.
The object of this invention is to provide a detachable handle which may be applied to a plane at the side thereof, so that when the plane is used upon its side the operator may have a convenient and effective means to hold the plane and apply to it power sufficient to cause it to operate efficiently in the intended manner. Heretofore in using tools of this character with the edge of the knife placed vertically it has been not only extremely awkward for the operator, but very difficult, to keep the plane in the proper position to get true and effective work. Frequently the thing to be planed is of such a shape or is so located that it cannot be placed upright to permit the plane to be used in the ordinary way, with the hired handle upright, and it is because on occasions it is necessary to use the plane on its side that I have found my improved detachable handle to be a feature of great convenience and utility.
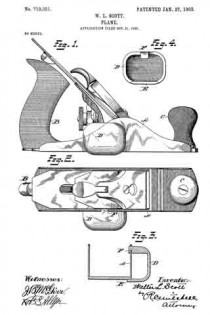
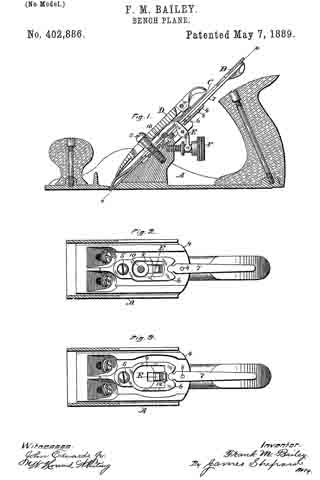
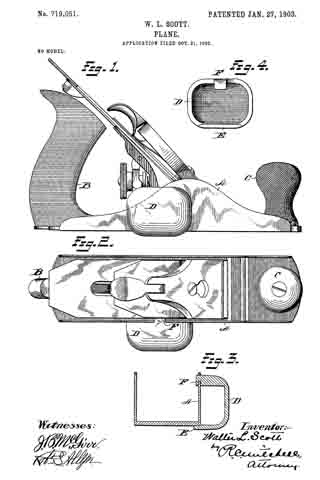
In the drawings, Figure 1 is a side elevation of a plane with the detachable handle applied thereto. Fig. 2 is a plan view. Fig. 3 is a cross-section of the plane-stock and detachable handle, as shown in Fig. 1. Fig. 4 is a view of the inside of the detachable handle.
A represents the stock of an iron plane. B is a handle permanently attached to the rear end thereof.
C is a front knob or handle, also usually permanently attached to the stock A. In ordinary use the operator grasps the two handles B C, The other details of the plane proper, such as the knife and the adjusting devices, it is unnecessary to describe in detail herein, because they constitute no part of this invention.
D is the body of a detachable handle, preferably in the form of a shell, since it provides a strong and light construction.
E is a lip on one side of the body D, the same being by preference of sufficient length to give a long flat bearing. Obviously the number of these lips E is immaterial. Two short lips spaced apart would give the same result. The lip E will for convenience of expression be termed herein the “fiat” lip. F is a hooked lip at the opposite side of the body D, the hook facing the flat lip E. Ordinarily the stock A of a metal plane is provided with cheek-pieces, one on each side, and these cheek-pieces are generally shaped as shown in Fig. 1, in which they incline upwardly from each end to a high point or crown.
In attaching the handle-body D the flat lip E is placed against the bottom of the plane-stock, and the handle is then pushed forward toward the highest part of the cheek-piece until the hooked lip F engages with it and may be wedged thereon, the hook of the lip F overstanding the upper edge of the cheek-piece and securing the handle in place on the side of the plane. The operator may then use the plane with one or both hands.
In case one hand is used the palm is placed against the rear side of the body D and the fingers are placed over the top of the plane, giving a secure grip. The position of the plane will then be on its side and the same may be pushed along the side or edge of the thing to be planed and the work done with ease and accuracy. In case the operator desires to use two hands he may grasp the solid handle B with one hand and the detachable handle D with the other, the latter taking the place of the knob-handle C. When the work is completed, the handle D may be easily removed by sliding the same backward and freeing the hook F from the cheek-piece of the stock.
Obviously the particular shape of the handle and its particular construction may be varied and modified in such ways as will suggest themselves to the mechanic skilled in the art without departure from the spirit and scope of this invention.
What I claim is —
1. A side handle for a plane comprising a body portion and means projecting from said body for detachably engaging the same at the side of a plane-stock.
2. A side handle for a plane comprising a body portion and means for frictionally engaging the same with the cheek-piece of the plane-stock.
3. A side handle for a plane comprising a body portion D, a flat lip on one side, and a lip on the opposite side said lips adapted to engage with the plane-stock.
4. A side handle for a plane comprising a body portion D, a flat lip at one edge thereof, and a hooked lip at the opposite edge thereof.
5. A side handle for a plane comprising a body portion, a lip on one edge thereof, a lip on the other side thereof, one of said lips being hooked.
Signed at San Francisco, California, this 10th day of October, 1902.
WALTER L. SCOTT.
Witnesses:
GEORGE PATTISON,
J. W. WRIGHT.